Exploring The Future of Weight Loss: Growth and Opportunities

The success of blockbuster GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs Ozempic, Wegovy, and Zepbound for weight loss has defined a new market in weight loss treatments, characterized by breakneck demand that periodically outpaces supply.
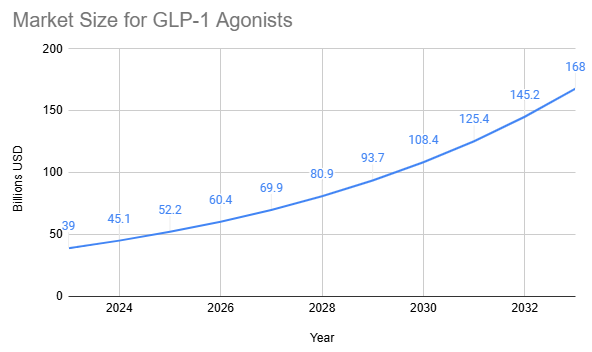
GLP-1 agonists represent the highest-growth segment of the weight loss market since their meteoric rise beginning in 2021. The global market for GLP-1 agonists for weight loss and diabetes is projected to reach $45 billion by year-end.
Globally, pharmaceutical companies are feverishly working to establish their presence in this burgeoning market, currently dominated by Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. This duopoly is expected to continue through 2026, at which point the market is projected to reach $60 billion.
By 2033, this class of drugs is projected to generate $168 billion in global sales, with North America accounting for 68% of this total.[1]
Behind the Market Boom
Obesity is considered the most prevalent health issue in the United States today, contributing to leading causes of death and disability such as heart attack, stroke, and diabetes. Recent figures indicate that 41.9% of adult Americans[2] and between 890 million and 1 billion people worldwide live with obesity.
Related medical costs in the United States reached nearly $173 billion in 2019 [3] and obesity-related health issues continue to escalate nationally. Worldwide obesity rates have doubled since 1980.
The benefits of controlling obesity extend beyond individual well-being to societal and public health. Obesity is a major contributor to chronic health problems, straining healthcare systems. These problems include type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, stroke, fatty liver disease, osteoarthritis, and mental health disorders.
Obesity-related care and associated health problems account for over 20% of annual healthcare expenditures in the United States. Obese individuals incur medical costs 30-40% higher than their normal-weight peers. Only 40% of young adults aged 17-24 are physically fit enough to enter manual labor or military service.
The Future of GLP-1 Agonists: Patents, Competition, and Innovation
GLP-1 agonists, a new class of weight loss drugs, evolved from treatments for diabetes. While not entirely new, these drugs have gained significant attention since 2021, with a series of approvals from the US Food and Drug Administration and the EU in 2021 and 2022.
These drugs mimic the naturally occurring hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and are patented by type of agonist: semaglutide, tirzepatide, and liraglutide. They not only regulate blood sugar levels but also bind to receptors in the brain to control appetite and to receptors in the gut to slow digestion, contributing to feelings of fullness.
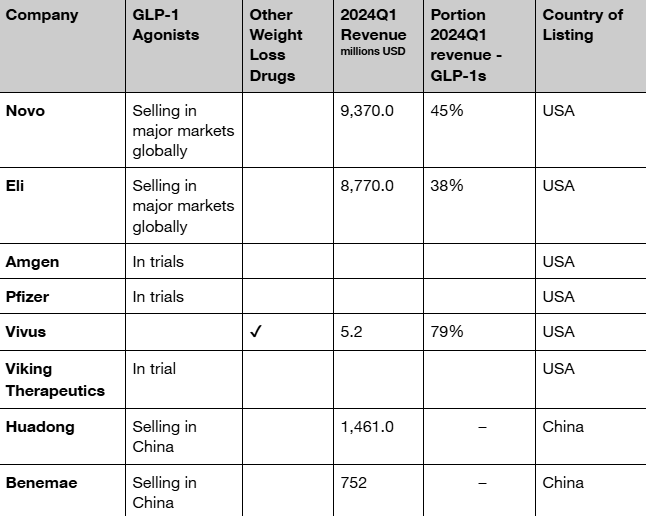
The global demand for GLP-1 agonists as both weight loss and diabetes treatments fuels the race to develop new drugs and capitalize on patent expirations. Novo Nordisk holds the patent for semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic), with generic versions expected to enter the market in the US and Canada, the two largest markets for GLP-1 agonists, as early as 2026.
Eli Lilly will maintain its lead for longer, with patents for tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound) expiring between 2031 and 2039. Amgen and Pfizer are currently developing GLP-1 agonist-based drugs and are in various stages of clinical trials.
In China, the patent for liraglutide has already expired, and the one for semaglutide will expire in 2026 in India and China.
Two major players in the Chinese market for GLP-1 agonists are Huadong Medicine with liraglutides and Benemae Pharmaceuticals with beinaglutides. Both companies began selling products in 2024.
The global anti-obesity drugs market size is projected to grow from USD 6.15 billion in 2024 to USD 37.94 billion by 2032, with two-thirds of the demand from the United States.[4]
Watch List: Promising Pharmaceuticals
BITA's Proprietary Data Team meticulously analyzes revenue streams across all industries including those related to pharmaceuticals, biotech, health and wellbeing, and identifies emerging growth opportunities such as GLP-1 agonists. BITA’s extensive universe of over 90 investment themes covers diverse sectors, including finance, technology, sustainability, social impact, food, health, leisure, sports, culture, and controversial business involvement.
In addition to comprehensive thematic analysis, BITA also tracks ESG data such as emissions, waste, and net-zero commitments.
References
Fortune Business Insights. “Anti-obesity Drugs Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, By Type (Prescription Drugs and OTC Drugs), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacy and Retail and Online Pharmacy), and Regional Forecast, 2024-2032”
https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/anti-obesity-drugs-market-104783
Global Market Insight. Anti-Obesity Drugs Market - By Product (Prescription, OTC), Action Pathway (Peripherally Acting, Centrally Acting), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Drug Stores) – Global Forecast (2024 – 2032)
https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/anti-obesity-drugs-market
GoodRx. Murdock, J. “The Latest Updates: 16 New Weight Loss Drugs on the Horizon”.
https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/weight-loss/new-weight-loss-drugs
Healthline. Cafasso, J. “How Does Obesity Affect the Body?”.
https://www.healthline.com/health/obesity/how-obesity-affects-body
Healthline. Mastroianni, B. “The Year’s Top Medical Breakthroughs in Weight Loss”.
https://www.healthline.com/health-news/top-medical-breakthroughs-weight-loss
HelpGuide.org. “How Excess Weight Affects Your Health”.
https://www.helpguide.org/wellness/weight-loss/how-excess-weight-affects-your-health
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Singh, G. et al. “Wegovy (semaglutide): a new weight loss drug for chronic weight management”.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8717485/
National Center for Biotechnology Information. The Surgeon General's Call To Action To Prevent and Decrease Overweight and Obesity. “Section 1: Overweight and Obesity as Public Health Problems in America”.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK44210/
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Tiwari, A. & Balasundaram, P. “Public Health Considerations Regarding Obesity”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572122/
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. “Health Risks of Overweight & Obesity”
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/adult-overweight-obesity/health-risks
Scientific America “xxxx”
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. Thomas, M. et al. “Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide Improves Beta-cell Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes”.
https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/106/2/388/6000489?login=false
U.S. Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. “Consequences of Obesity”.
https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/consequences.html
World Health Organization. “Obesity: Health consequences of being overweight”.

