The Controversial Weapons Landscape Today - More Activity than in Recent Decades

● Controversial weapons describe those weapons which cause disproportionate damage to citizens, as they do not differentiate between military and civilian targets.
● The threat of nuclear weapons rises as Russia warns it will use nuclear weapons should Ukraine’s (and NATO’s) offensive take Russian land. Ukraine, Russia and Syria are among the countries that use cluster bombs.
● BITA’s deep and thorough Controversial Weapons research of public companies gives our clients the necessary information to make informed investment decisions pertaining to companies that take part in development and manufacturing of controversial weapons.






Global military spending rose by 3.7% in real terms to a high of USD 2.24 trillion in 2022, with 56% of it coming from the United States, China, and Russia, which are the top spenders on this matter (PwC). The defense industry has experienced growth in demand driven mainly by the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The war has pushed many nations to re-evaluate and increase their military budgets, budgets which are allocated not only for their own military defenses but also to produce and trade munitions and military technologies. With over 40 countries sending military aid to Ukraine, the industry has also suffered a supply shortage, leaving stocks of missiles, rockets, drones, anti-aircraft, and surface-to-air defense systems severely depleted.
One of the consequences of the supply shortages is the recent decision by the United States to supply Ukraine with cluster munitions to face the Russian invasion and “level the field”. The announcement has sparked a heated debate on the morality of their use, as cluster bombs, even the ones with reduced dud rate, are classified as controversial weapons.
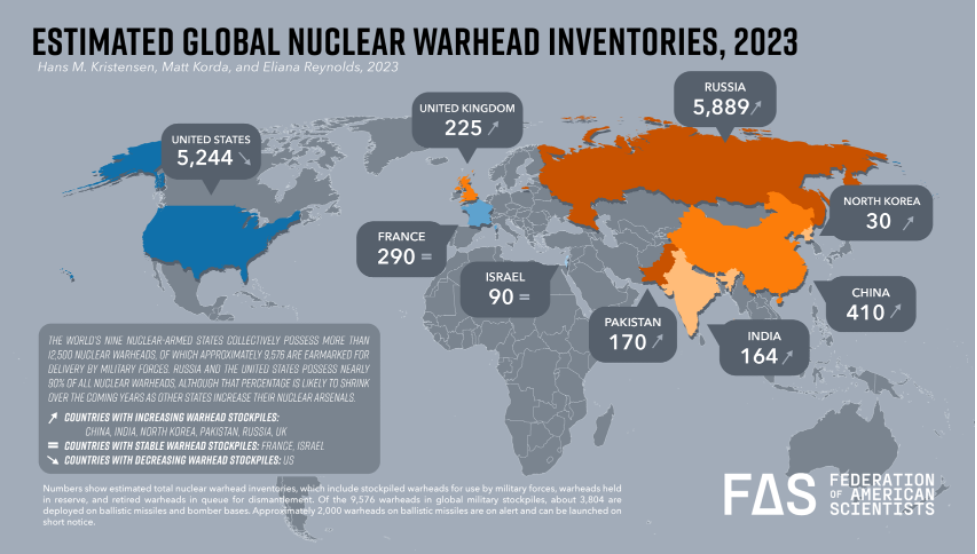
The term “controversial weapons” refers to the types of weapons that cause disproportionate damage to citizens, as they do not differentiate between military and civilian targets. Some refer to them as weapons of mass destruction. The use of these weapons tends to dismiss the collateral damage they cause, and therefore, they are a great source of concern globally. These concerns have resulted in the signing of many treaties that prohibit the production, use, stockpile, proliferation, and sometimes the complete ban of these weapons. As shown in Table N° 1, not every country in the world has signed (or ratified) the treaties, but the majority of countries show interest in the regulation of controversial weapons.
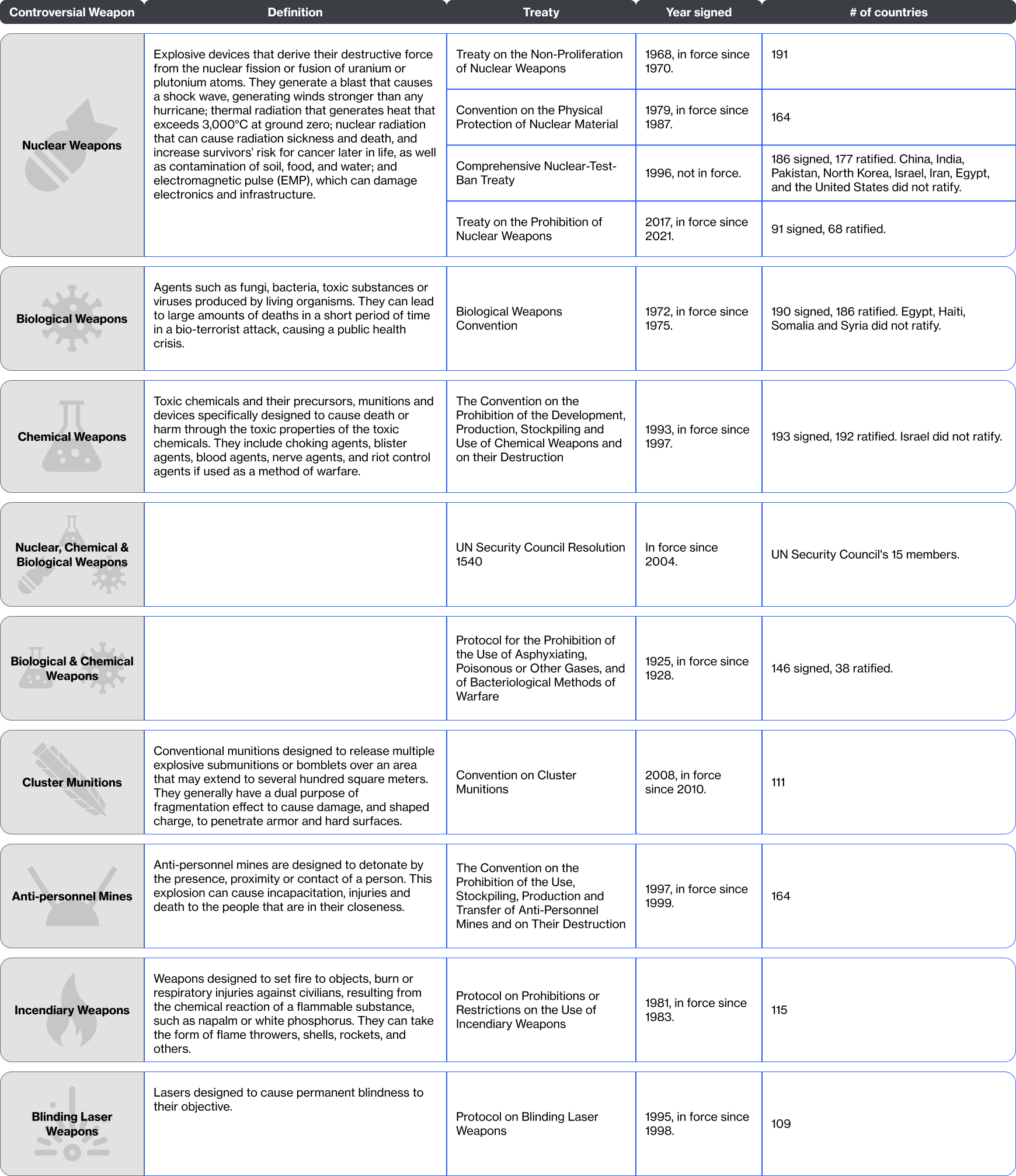
Currently, the USA and Russia possess approximately 89% of the world’s total inventory of nuclear weapons, according to the Federation of American Scientists (FAS) (see Figure N°1), followed by China and France. As the Ukraine-Russia conflict progresses, the threat of the use of nuclear weapons rises, as the senior Russian official, and former Russian president, Dmitry Medvedev, declared in July 2023, stating that Russia would use nuclear weapons if Ukraine’s (and NATO’s) offensive manages to take Russian land, even though the U.S. has warned Russia against it. The use of cluster bombs has been reported not only by Ukraine (which currently holds the highest number of casualties by this weapon), but also by Russia and Syria, with childrens among the majority of victims.
Identifying the Largest Companies Involved in Controversial Weapons - Given Limited Disclosure on the Topic
The aforementioned conventions and treaties aim to limit or outright ban controversial weapons. Countries that do not ratify or sign onto them have national security programs that consider the development of some of these weapons. The execution of these programs requires that contracted companies, public or private, participate in their production and maintenance processes, including parts, engineering, and technologies. Some of the biggest publicly listed companies involved in and self-identifying in these activities (see Sources, below) are:
- Honeywell International Inc.: with a market capitalization of 125.65 billion USD, the American multinational manages and operates the Kansas City National Security Campus (KCNSC), which maintains the U.S. nuclear stockpile, providing over 80% of all non-nuclear components in support of the U.S. nuclear deterrence.
- The Boeing Company: the American aerospace and defense multinational has a market capitalization of 118.19 billion USD and, since 1958, has designed, developed, delivered and sustained three generations of Minuteman intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM) for the U.S. Air Force. The latest version of the Minuteman missiles, the Minuteman III, carry thermonuclear warheads.
- Airbus SE: the French multinational (market capitalization of 103.08 billion USD) operates a joint aerospace venture with the French multinational Safran SA (market capitalization of 61.40 billion USD) called ArianeGroup. ArianeGroup acts as prime contractor on behalf of the French defense procurement agency DGA for the M51 programme for the French Navy’s Strategic Oceanic Force, and is responsible for the research, design, development and production of the M51 missiles for the French nuclear deterrent force.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation: the American company, mainly involved in aerospace, defense and technology, has developed ICBMs since 1955, such as the Atlas, Titan and MX Peacekeeper. It is the provider of the reentry systems for the Minuteman III, as well as ground command and control systems. It also produces the Trident II D5 Fleet Ballistic Missile (FBM). The company has a market capitalization of 103.99 billion USD.
- RTX Corporation: an American aerospace and defense conglomerate, with a market capitalization of 103.47 billion USD, is involved in nuclear missiles through its subsidiary Collins Aerospace which is working on the delivery of the launch platform for the LGM-35A Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missile, which will replace the Minuteman III. RTX Corporation is also developing the Long-Range Standoff (LRSO) cruise missile, which will be nuclear-armed.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation: the company is the developer of the previously mentioned LGM-35A Sentinel ICBM, which will modernize the U.S.’ nuclear triad. The American company has a market capitalization of 64.31 billion USD.
Despite efforts to control production of the weapons, the number of publicly listed companies involved in the development, manufacturing, parts, and maintenance of controversial weapons is long and distributed among several markets. BITA’s ESG Team researches the controversial weapons landscape to find these companies and provide the information to our clients for investment screening purposes. BITA’s controversial universe coverage spans firearms, adult entertainment, gambling, recreational drugs, nuclear, alcohol, non-renewable energy and topics in health.
Sources:
PwC: https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industrial-products/publications/assets/pwc-aerospace-defense-annual-industry-performance-outlook-2023.pdf
A Guide to Cluster Munitions: https://www.clusterconvention.org/files/publications/A-Guide-to-Cluster-Munitions.pdf
Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty: https://www.ctbto.org/our-mission/the-treaty
Arms Control Association: https://www.armscontrol.org/factsheets/test-ban-treaty-at-a-glance#:~:text=The treaty was opened for,Egypt%2C and the United States.
Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons: https://www.nti.org/education-center/treaties-and-regimes/treaty-on-the-prohibition-of-nuclear-weapons/
Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons: https://disarmament.unoda.org/wmd/nuclear/npt/
Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material: https://www.oecd-nea.org/jcms/pl_29139/convention-on-the-physical-protection-of-nuclear-material-cppnm
Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use of Asphyxiating, Poisonous or Other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare: https://www.nti.org/education-center/treaties-and-regimes/protocol-prohibition-use-war-asphyxiating-poisonous-or-other-gasses-and-bacteriological-methods-warfare-geneva-protocol/
Biological Weapons Convention: https://www.nti.org/education-center/treaties-and-regimes/convention-prohibition-development-production-and-stockpiling-bacteriological-biological-and-toxin-weapons-btwc/#:~:text=The treaty prohibits the development,disseminate such agents or toxins.
UN Security Council Resolution 1540 At a Glance: https://www.armscontrol.org/factsheets/1540
Chemical Weapons Convention: https://www.opcw.org/chemical-weapons-convention
The Convention on the Prohibition of the Use, Stockpiling, Production and Transfer of Anti-Personnel Mines and on Their Destruction: https://www.apminebanconvention.org/en/the-convention/history-and-text/
The Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons: https://disarmament.unoda.org/the-convention-on-certain-conventional-weapons
High Contracting Parties and Signatories CCW: https://disarmament.unoda.org/the-convention-on-certain-conventional-weapons/high-contracting-parties-and-signatories-ccw/
Nuclear weapons: a beginner’s guide to the threats: https://www.sgr.org.uk/resources/nuclear-weapons-beginner-s-guide-threats
Status Of World Nuclear Forces: https://fas.org/initiative/status-world-nuclear-forces/
Biological weapons: https://www.who.int/health-topics/biological-weapons#tab=tab_1
Biological Weapons Nonproliferation: https://tutorials.nti.org/biological-weapons-nonproliferation/
Incendiary Weapons: https://disarmament.unoda.org/convarms/incendiary-weapons/#:~:text=Incendiary weapons are weapons or,as napalm or white phosphorus.
Behind Washington’s decision to supply cluster bombs to Ukraine : https://www.newyorker.com/news/daily-comment/behind-washingtons-decision-to-supply-cluster-bombs-to-ukraine
Delivering Proven and Trusted Innovation to National Security: https://aerospace.honeywell.com/content/dam/aerobt/en/documents/learn/platforms/brochures/N61-2069-000-000_NuclearDeterrentSummit2019-br.pdf
Kansas City National Security Campus: https://kcnsc.doe.gov/missions/about-us
Airbus SE Universal Registration Document 2022: https://www.airbus.com/sites/g/files/jlcbta136/files/2023-04/Airbus Universal Registration Document 2022_0.pdf
Ensuring Peace through Strength: https://www.boeing.com/defense/strategic-deterrence-systems/
M51: A central part of French deterrence: https://www.ariane.group/en/defense/m51/
US Air Force selects Raytheon Missiles & Defense to develop Long-Range Standoff weapon: https://raytheon.mediaroom.com/2020-04-20-US-Air-Force-selects-Raytheon-Missiles-Defense-to-develop-Long-Range-Standoff-weapon
Collins Aerospace to deliver launch platform for ICBM modernization program: https://www.collinsaerospace.com/news/news/2020/11/collins-deliver-launch-platform-icbm-modernization-program
LGM-35A Sentinel Intercontinental Ballistic Missile, USA: https://www.airforce-technology.com/projects/lgm-35a-sentinel-intercontinental-ballistic-missile-usa/
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM): https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/icbm.html
Trident II D5: https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/trident-ii-d5-fleet-ballistic-missile.html#:~:text=First deployed in 1990%2C the,the missile and support equipment
Sentinel – The Ground Based Strategic Deterrent: https://www.northropgrumman.com/space/sentinel
Medvedev says Russia could use nuclear weapon if Ukraine’s fightback succeeds in latest threat: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/07/31/europe/medvedev-russia-nuclear-weapons-intl-hnk/index.html
Ukraine Surpasses Syria as Country With Most Cluster-Munition Casualties in the World: https://time.com/6310759/ukraine-syria-cluster-munition-casualties/

